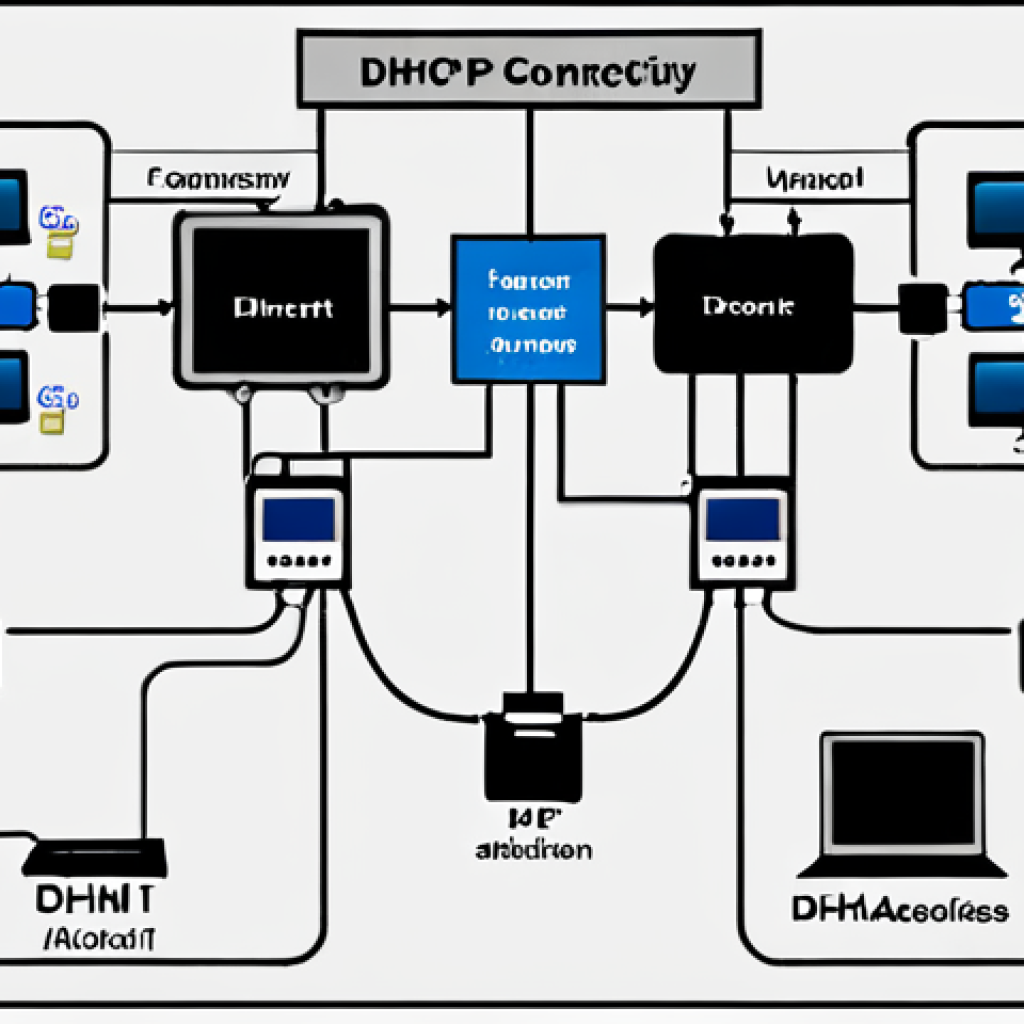
Ever wondered how your computer magically gets an IP address and knows where to go on the internet? It all boils down to two unsung heroes of the network world: DNS (Domain Name System) and DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol).
Think of DHCP as the friendly postman who delivers your computer’s unique address, and DNS as the handy phonebook that translates website names into those numerical addresses.
They work hand-in-hand to make browsing the web a breeze. From my own experience troubleshooting network issues, understanding these protocols is absolutely crucial.
Without them, the internet as we know it would grind to a halt, and trust me, nobody wants that! The current trend leans towards enhanced security in both DNS and DHCP, anticipating future needs for faster and more secure browsing as more and more devices connect to the internet.
Let’s dive deeper and get a clearer picture in the article below!
Navigating the Web’s Underpinnings: Understanding Digital Addresses
The Magic Behind Automatic Network Configuration

Have you ever wondered how your devices effortlessly connect to a network without you manually assigning an IP address? That’s DHCP at play. I remember setting up a small office network years ago and forgetting to enable DHCP on the router.
The chaos that ensued as I manually configured each computer was a harsh lesson in appreciating DHCP’s convenience! It’s like having a smart system that automatically assigns and manages IP addresses, subnet masks, default gateways, and DNS server addresses.
This automation reduces the risk of configuration errors and IP address conflicts, making network administration significantly smoother.
DHCP Lease Process: A Closer Look
The DHCP lease process is how your device obtains and uses an IP address. It begins when a device requests an IP address from a DHCP server. The server then offers an available IP address to the device.
Once the device accepts the offer, the server grants a lease, which is a temporary assignment of the IP address. The device can then use this IP address for a specified period.
Before the lease expires, the device attempts to renew the lease, ensuring uninterrupted network connectivity. Think of it like renting an apartment – you get the space for a set period, and you renew the lease to stay longer!
Benefits of DHCP in Modern Networks
The benefits of DHCP are numerous, especially in today’s dynamic network environments. Imagine trying to manage IP addresses manually for hundreds of devices in a large organization – it would be a logistical nightmare!
DHCP simplifies network administration by automatically assigning IP addresses, preventing conflicts and reducing administrative overhead. DHCP also supports dynamic IP address allocation, allowing devices to move freely within the network without requiring reconfiguration.
I’ve seen firsthand how DHCP has streamlined network management in several organizations, saving time and resources.
Deciphering Domain Names: How DNS Makes the Internet User-Friendly
Imagine having to type in a string of numbers every time you wanted to visit your favorite website. It sounds absurd, right? That’s where DNS comes to the rescue.
It translates human-readable domain names like “google.com” into IP addresses that computers understand. I recall explaining DNS to my non-tech-savvy aunt, and the analogy that clicked was comparing it to a phonebook: you look up a name (domain) to find the corresponding number (IP address).
Without DNS, browsing the internet would be an exercise in memorizing countless IP addresses.
DNS Resolution Process: Step-by-Step
The DNS resolution process is a series of steps that occur behind the scenes when you type a domain name into your browser. First, your computer queries a DNS resolver, which is typically provided by your internet service provider (ISP).
The resolver then queries a root DNS server, which directs it to the appropriate top-level domain (TLD) server (e.g., .com, .org). The TLD server then points the resolver to the authoritative DNS server for the domain.
Finally, the authoritative DNS server provides the IP address associated with the domain name, allowing your browser to connect to the website. It’s like a detective following clues to find the right location!
Common DNS Record Types and Their Purposes
DNS records are entries that contain information about a domain, such as its IP address, mail servers, and other settings. Different types of DNS records serve different purposes.
A records map domain names to IPv4 addresses, while AAAA records map domain names to IPv6 addresses. MX records specify the mail servers responsible for accepting email messages for the domain.
CNAME records create aliases for domain names, allowing multiple domain names to point to the same IP address. Understanding these record types is crucial for managing and troubleshooting DNS issues.
I once spent hours debugging a website that was down because of a misconfigured A record – a painful but valuable learning experience!
Enhancing Network Security: DNSSEC and DHCP Snooping
As network threats become more sophisticated, securing DNS and DHCP is paramount. DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions) adds cryptographic signatures to DNS records, verifying the authenticity of DNS responses and preventing DNS spoofing attacks.
DHCP snooping is a security feature that filters DHCP messages, preventing rogue DHCP servers from assigning malicious IP addresses. I’ve seen firsthand how these security measures can significantly reduce the risk of network attacks and data breaches.
Implementing DNSSEC for Enhanced Security
Implementing DNSSEC involves several steps, including generating cryptographic keys, signing DNS records, and configuring DNS servers to validate DNSSEC signatures.
While the implementation process can be complex, the added security benefits are well worth the effort. DNSSEC ensures that DNS responses are authentic and untampered with, preventing attackers from redirecting users to malicious websites or intercepting sensitive data.
I always recommend organizations prioritize DNSSEC implementation to protect their online presence.
DHCP Snooping and Its Role in Preventing Rogue DHCP Servers
DHCP snooping is a security feature that operates at the data link layer, filtering DHCP messages based on predefined policies. It prevents rogue DHCP servers from assigning IP addresses to clients, mitigating the risk of man-in-the-middle attacks and other network security threats.
DHCP snooping typically involves configuring trusted and untrusted ports on network switches. Only DHCP messages received on trusted ports are allowed to pass through, while messages received on untrusted ports are dropped.
I’ve seen DHCP snooping effectively block rogue DHCP servers in several network environments, enhancing overall security.
Troubleshooting Common DNS and DHCP Issues
Despite their importance, DNS and DHCP are not immune to problems. Common issues include DNS resolution failures, DHCP server outages, IP address conflicts, and incorrect DNS or DHCP configurations.
Troubleshooting these issues requires a systematic approach and a good understanding of network protocols. I’ve developed a troubleshooting checklist over the years that helps me quickly diagnose and resolve DNS and DHCP problems.
Diagnosing and Resolving DNS Resolution Failures
DNS resolution failures can occur for various reasons, such as incorrect DNS server settings, network connectivity problems, or DNS server outages. To diagnose a DNS resolution failure, start by verifying your DNS server settings and ensuring that your network connection is working properly.
You can use command-line tools like or to query DNS servers and check for errors. If the problem persists, try flushing your DNS cache or switching to a different DNS server.
I once spent hours troubleshooting a DNS resolution issue only to discover that the problem was a simple typo in the DNS server address!
Handling DHCP Server Outages and IP Address Conflicts
DHCP server outages can disrupt network connectivity for all devices that rely on DHCP for IP address assignment. To mitigate the impact of a DHCP server outage, consider implementing DHCP redundancy by setting up multiple DHCP servers.
IP address conflicts occur when two devices are assigned the same IP address, leading to network connectivity problems. To prevent IP address conflicts, ensure that your DHCP server has a sufficient IP address pool and that IP addresses are not manually assigned to devices without proper coordination.
I’ve learned the hard way that careful planning and monitoring are essential for preventing DHCP server outages and IP address conflicts. Here’s a table summarizing the key differences between DNS and DHCP:
| Feature | DNS (Domain Name System) | DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Translates domain names to IP addresses | Automatically assigns IP addresses and other network configuration parameters |
| Function | Provides a directory of domain names and their corresponding IP addresses | Manages a pool of IP addresses and leases them to devices on the network |
| Dependency | Essential for accessing websites and online resources using domain names | Essential for simplifying network administration and preventing IP address conflicts |
| Security | DNSSEC provides authentication and integrity for DNS responses | DHCP snooping prevents rogue DHCP servers from assigning malicious IP addresses |
| Troubleshooting | Involves verifying DNS server settings, flushing DNS cache, and querying DNS servers | Involves checking DHCP server availability, IP address conflicts, and lease expirations |
The Future of DNS and DHCP: Trends and Innovations
The future of DNS and DHCP is characterized by a focus on enhanced security, scalability, and automation. Emerging trends include the adoption of DNS over HTTPS (DoH) and DNS over TLS (DoT) for encrypted DNS communication, as well as the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) for automated network management and threat detection.
I believe that these innovations will play a crucial role in shaping the future of networking.
DNS over HTTPS (DoH) and DNS over TLS (DoT) for Encrypted Communication
DNS over HTTPS (DoH) and DNS over TLS (DoT) are protocols that encrypt DNS queries and responses, protecting them from eavesdropping and tampering. DoH encapsulates DNS queries within HTTPS traffic, while DoT uses TLS encryption directly for DNS traffic.
These protocols enhance privacy and security by preventing attackers from intercepting or modifying DNS traffic. I see DoH and DoT as essential tools for protecting user privacy in an increasingly interconnected world.
AI and ML for Automated Network Management and Threat Detection
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are transforming network management by enabling automation, predictive analytics, and threat detection.
AI and ML algorithms can analyze network traffic patterns, identify anomalies, and predict potential security threats. They can also automate routine network management tasks, such as IP address allocation, DNS configuration, and performance optimization.
I believe that AI and ML will play a significant role in simplifying network management and improving network security in the years to come. By understanding the roles of DNS and DHCP, and staying abreast of the latest trends and innovations, you can ensure that your network is secure, reliable, and efficient.
These protocols are the unsung heroes of the internet, working silently behind the scenes to make our online experiences seamless. Navigating the intricate world of DNS and DHCP might seem daunting at first, but understanding these core network components is crucial for anyone looking to build and maintain a robust and secure online environment.
From ensuring seamless website access to managing IP addresses efficiently, DNS and DHCP play pivotal roles in our digital lives. I hope this exploration has shed some light on their importance and empowered you to tackle networking challenges with confidence.
Wrapping Up
As we conclude, remember that the digital landscape is ever-evolving. Keeping up with the latest in DNS and DHCP will not only enhance your network’s performance but also fortify its security. I encourage you to explore further and stay informed, as these technologies are the foundation upon which our interconnected world thrives. Embrace the challenge and watch your network skills soar!
Useful Information to Know
1. Free DNS Servers: Consider using free and reliable DNS servers like Google Public DNS (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare DNS (1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1) for improved speed and security.
2. DHCP Reservation: Use DHCP reservation to assign a permanent IP address to frequently used devices like printers or servers. This ensures consistent network accessibility.
3. DNS Leak Test: Regularly perform DNS leak tests to ensure your VPN is properly masking your DNS queries and protecting your privacy. Several online tools can help with this.
4. Renewing IP Address: If you’re having network issues, try renewing your IP address. On Windows, use followed by in the command prompt. On macOS, go to System Preferences> Network, select your connection, and click “Renew DHCP Lease.”
5. DHCP Scope: When configuring DHCP, plan your IP address scope carefully to accommodate current and future network growth. Leave some buffer to avoid future IP address exhaustion.
Key Takeaways
DHCP Automates IP Management: DHCP simplifies network administration by automatically assigning IP addresses, preventing conflicts and reducing overhead.
DNS Translates Domains: DNS translates human-readable domain names into IP addresses, making the internet user-friendly.
Security is Paramount: DNSSEC and DHCP snooping are essential security measures to protect against DNS spoofing and rogue DHCP servers.
Troubleshooting is Key: A systematic approach is crucial for diagnosing and resolving DNS and DHCP issues.
The Future is Secure and Automated: Emerging trends like DoH/DoT and AI/ML are enhancing security, scalability, and automation in DNS and DHCP.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 📖
Q: So, if my internet suddenly stops working, is DHCP or DNS usually the culprit?
A: From personal experience, it could honestly be either! But here’s a simple way to start troubleshooting. If you can access some websites by directly typing in their IP address (like 8.8.8.8, Google’s public DNS), but not by typing in the website name (like google.com), then DNS is likely the issue.
However, if you can’t even get online at all, it’s more likely a DHCP problem – your computer probably didn’t get an IP address in the first place. Think of it like this: DNS is the phonebook, DHCP is getting a phone line to begin with.
Q: You mentioned enhanced security in DNS and DHCP – what does that actually look like in practice?
A: Great question! Security measures can include things like DNSSEC (DNS Security Extensions), which adds a digital signature to DNS data to prevent tampering.
For DHCP, security might involve preventing rogue DHCP servers from assigning incorrect or malicious IP addresses on your network. In real-world terms, imagine your local coffee shop’s Wi-Fi.
They might use DHCP snooping to ensure only authorized DHCP servers can assign IP addresses, preventing someone from setting up a fake Wi-Fi hotspot to steal your data.
Basically, it’s all about verifying the authenticity of the information being exchanged and preventing unauthorized access.
Q: Okay, so if these protocols are so important, can I actually see them in action? Like, on my own computer?
A: Absolutely! On Windows, you can open the command prompt and type “ipconfig /all” to see your DHCP settings, including the IP address your computer has been assigned, the address of your DHCP server, and your DNS server addresses.
On a Mac, you can find similar information in System Preferences under Network. It’s like peeking under the hood of your car – you might not understand everything you see, but you can definitely get a glimpse of how DHCP and DNS are working behind the scenes to connect you to the internet.
Personally, digging into these settings has helped me diagnose countless connection problems over the years, and it’s surprisingly empowering once you get the hang of it.
📚 References
Wikipedia Encyclopedia
구글 검색 결과
구글 검색 결과
구글 검색 결과
구글 검색 결과
구글 검색 결과